-
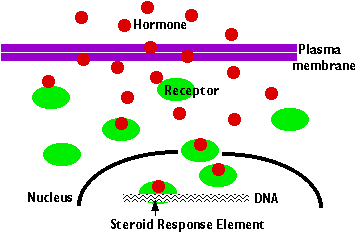
The hormone enters the cell as it is lipid soluble.
-
It binds to its receptor in the cytoplasm..
-
The hormon receptor compound then enters the nucleus, where it binds to gene promoter sequences of the genes responsive to the hormone. (sometimes the hormone/receptor complex binds to a second receptor).
-
This binding turns genes on or off, depending on the particular hormone and action.
-
The cell begins to produce the appropriate gene products or reduces the production of the approriate gene products.