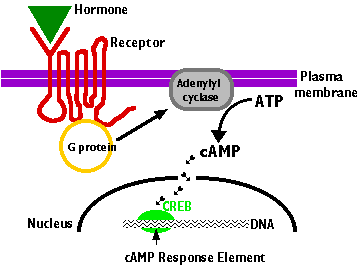
| |
- The hormone binds to the extracellular portion of the
receptor.
- Binding of the hormone to the receptor activates a
G protein associated with the cytoplasmic C-terminal. This initiates
the production of a "second messenger". The most common of
these are cyclic AMP, (cAMP) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3).
- The second messenger, in turn, initiates a series of
intracellular events such as phosphorylation and activation of enzymes
and release of Ca2+ stores within the cytoplasm
- In the case of cAMP, these enzymatic changes activate
a transcription factor (CREB, cAMP response element binding protein)
- CREB binds to its response element in the promoters
of genes that are able to respond to the hormone turning on gene transcription.
- The cell begins to produce the appropriate gene products
in response to the hormonal signal it had received at its surface.
|