|
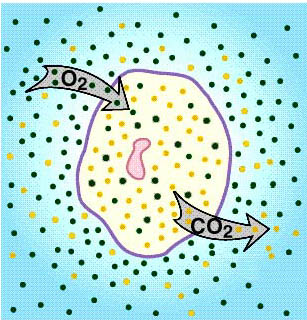
As the cell membrane is composed
mainly of a bilayer of phospholipid, lipid
soluble molecules can diffuse through it very
easily.
This is especially thrue for gases
(O2, CO2 and N2)
that are all lipid soluble.
In the cell, Oxygen diffuses in
while carbon dioxide diffuses out, down their
respective concentration gradients.
|
|